MAKE A MEME
View Large Image
| View Original: | Conant-Beyer Generalization of the Pythagorean Theorem for a set of 1-D objects.gif (357x305) | |||
| Download: | Original | Medium | Small | Thumb |
| Courtesy of: | commons.wikimedia.org | More Like This | ||
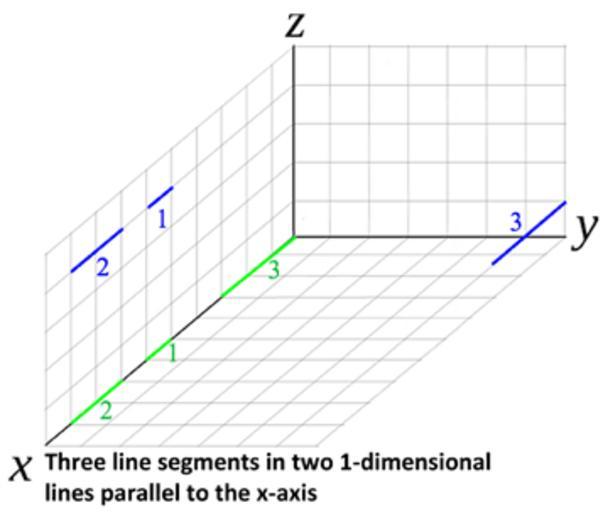
| Keywords: Conant-Beyer Generalization of the Pythagorean Theorem for a set of 1-D objects.gif en Conant-Beyer Generalization for the Pythagorean theorem applied to a set of 1-D objects The total length squared of a set of line segments shown in blue can be calculated by projecting the set of lines onto the x y and z coordinate axes calculating the total length of each projected set shown in green then squaring them and adding them together <br> a<sup>2</sup> + b<sup>2</sup> + c<sup>2</sup> d<sup>2</sup><br> where a b and c represent total lengths of the line segment sets on the x- y- and z- axes and d the total length of the original line segment set 2015-10-26 own Tripthelight42 other versions cc-zero Pythagorean theorem Uploaded with UploadWizard Generalizations of Pythagorean theorem | ||||