MAKE A MEME
View Large Image
| View Original: | Ebola Pathenogensis.svg (600x1000) | |||
| Download: | Original | Medium | Small | Thumb |
| Courtesy of: | commons.wikimedia.org | More Like This | ||
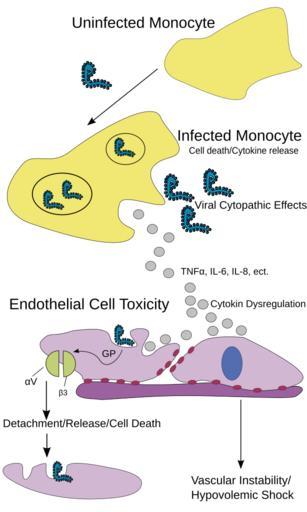
| Keywords: Ebola Pathenogensis.svg en Host immune responses to Ebola virus and cell damage due to direct infection of monocytes and macrophages cause the release of cytokines associated with inflammation and fever Infection of endothelial cells also induces a cytopathic effect and damage to the endothelial barrier that together with cytokine effects leads to the loss of vascular integrity Transient expression of Ebola virus GP in human umbilical vein endothelial cells or 293T cells causes a reduction of specific integrins primary molecules responsible for cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix and immune molecules on the cell surface Cytokine dysregulation and virus infection may synergize at the endothelial surface promoting hemorrhage and vasomotor collapse Nancy Sullivan Zhi-Yong Yang and Gary J Nabel; http //jvi asm org/cgi/reprint/77/18/9733 pdf ChyranandChloe 2009-08-06 Ebola pathogenesis 293T cells | ||||