MAKE A MEME
View Large Image
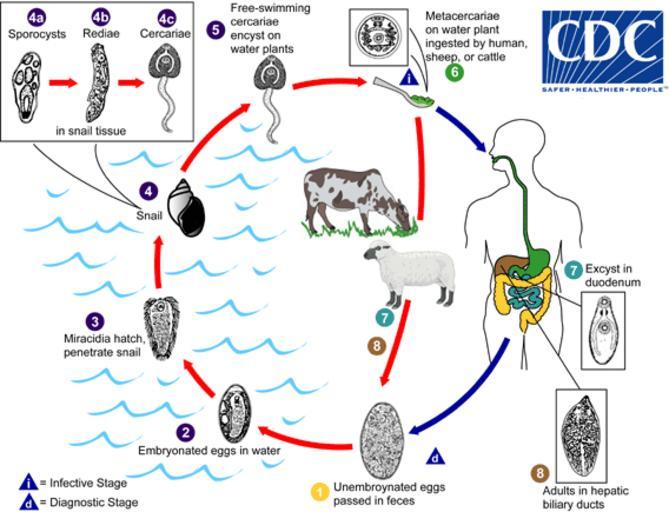
| View Original: | Fasciola_LifeCycle_2013.png (568x435) | |||
| Download: | Original | Medium | Small | Thumb |
| Courtesy of: | commons.wikimedia.org | More Like This | ||
| Keywords: Fasciola LifeCycle 2013.png en Immature eggs are discharged in the biliary ducts and in the stool The number 1 Eggs become embryonated in water The number 2 eggs release miracidia The number 3 which invade a suitable snail intermediate host The number 4 including the genera Galba Fossaria and Pseudosuccinea In the snail the parasites undergo several developmental stages sporocysts The number 4a rediae The number 4b and cercariae The number 4c The cercariae are released from the snail The number 5 and encyst as metacercariae on aquatic vegetation or other surfaces Mammals acquire the infection by eating vegetation containing metacercariae Humans can become infected by ingesting metacercariae-containing freshwater plants especially watercress The number 6 After ingestion the metacercariae excyst in the duodenum The number 7 and migrate through the intestinal wall the peritoneal cavity and the liver parenchyma into the biliary ducts where they develop into adults The number 8 In humans maturation from metacercariae into adult flukes takes approximately 3 to 4 months The adult flukes Fasciola hepatica up to 30 mm by 13 mm; F gigantica up to 75 mm reside in the large biliary ducts of the mammalian host Fasciola hepatica infect various animal species mostly herbivores N/A www cdc gov/dpdx/fascioliasis/index html CDC other versions PD-USGov Uploaded with UploadWizard Fascioliasis CDC lifecycles Life cycle of Fasciola hepatica | ||||