MAKE A MEME
View Large Image
| View Original: | Induction coil waveforms with capacitor.svg (664x661) | |||
| Download: | Original | Medium | Small | Thumb |
| Courtesy of: | commons.wikimedia.org | More Like This | ||
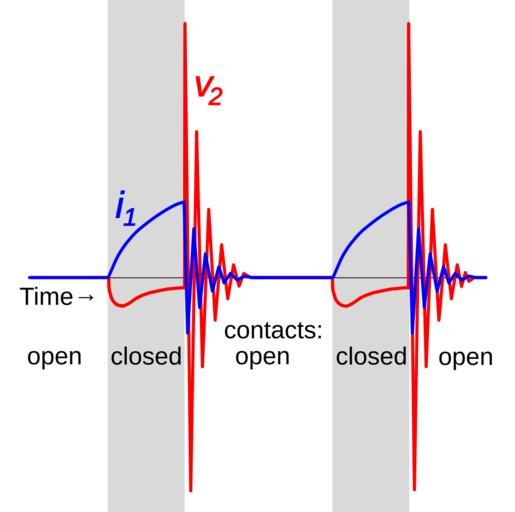
| Keywords: Induction coil waveforms with capacitor.svg induction coil demonstrating how the coil's interrupter works to generate the high voltages The <font color blue >blue</font> trace <font color blue >i<sub>1</sub></font> is the current in the coil's primary winding It is broken periodically by a vibrating contact in the primary circuit called an interrupter The changes in current create a changing magnetic flux in the coil which induces a high voltage in the secondary coil <font color red >v<sub>2</sub></font> shown in <font color red >red</font> The voltage induced in the secondary is proportional to the rate of change of the primary current Both the closing and opening of the interrupter contacts induce pulses of voltage of opposite polarity in the secondary But the current change is much more abrupt on the opening or break of the contacts and this generates the high voltage spikes produced by the coil <br /><br /> The interrupter has a capacitor across its contacts which increases the rate of current change on break and thus produces much higher secondary voltages The capacitor and primary winding function as a tuned circuit and on break produces a decaying sinusoidal current in the primary As a result the secondary voltage is also a decaying sinusoid <br /><br /> Informatin from http //books google com/books id e-hMAAAAMAAJ pg PA3 Louis Denton Bliss 1922 Theoretical and practical electrical engineering 2nd Ed The Bliss Electrical School p 3 fig 676 2014-05-19 16 20 11 own Chetvorno cc-zero Uploaded with UploadWizard Induction coils | ||||